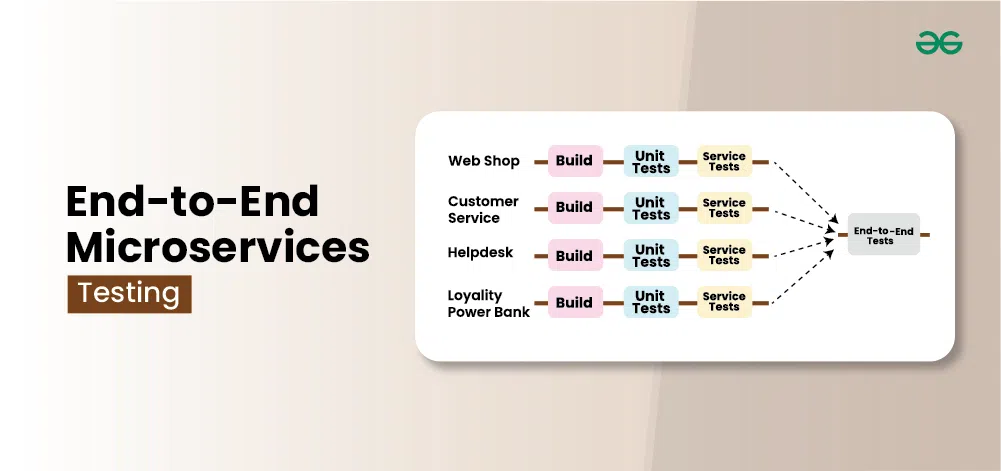
Microservices architectures have become the default foundation for modern enterprise platforms. They promise scalability, faster releases, and independent deployments. Yet for many organizations, this shift has introduced a new problem: end-to-end testing chaos.
As the number of services grows, traditional end-to-end (E2E) testing becomes slow, brittle, and expensive. Test suites break frequently, environments become unstable, and release confidence drops. This is why enterprises are rethinking how software testing services are applied to microservices—moving away from monolithic E2E tests toward smarter, risk-driven strategies.
For CTOs and QA leaders, the real question is no longer whether to test end-to-end, but how to do it without undermining delivery speed and system reliability.
Why End-to-End Testing Breaks Down in Microservices
The False Promise of Full Coverage
In monolithic systems, E2E testing validated complete business flows with reasonable effort. In microservices, the same approach creates:
- Long test execution cycles
- Fragile dependencies across teams
- Frequent false failures
- High maintenance overhead
This is where many enterprises realize that scaling E2E testing linearly does not scale quality. Mature qa testing services now emphasize precision over volume.
Microservices Multiply Test Complexity
Every service adds:
- Independent release cycles
- Network dependencies
- Data ownership boundaries
- Integration points
Testing everything together all the time leads to test chaos—slowing innovation rather than enabling it.
What Enterprise Decision Makers Are Actively Searching For
C-level leaders and QA heads are asking:
- How much end-to-end testing is actually necessary?
- How do we reduce flaky tests without losing coverage?
- How do we test microservices in CI/CD pipelines?
- How do we balance speed, quality, and risk?
The answer lies in modern quality engineering services that redefine the role of E2E testing in distributed systems.
Rethinking End-to-End Testing: A Strategic Shift
The Testing Pyramid Still Matters—But It Evolves
In microservices, enterprises are adopting:
- Strong unit and service-level tests
- Contract and API testing
- Limited, high-value E2E scenarios
Rather than eliminating E2E tests, leading software testing services teams focus on business-critical journeys only.
Define “End-to-End” by Business Outcome
Instead of testing every integration path, enterprises identify:
- Revenue-impacting workflows
- Regulatory and compliance paths
- Customer-facing journeys
This ensures E2E tests validate what matters most to the business—not just technical completeness.
Modern QA Strategies to Avoid Test Chaos
Contract Testing as the First Line of Defense
Contract testing validates interactions between services without requiring full system integration. It:
- Detects breaking changes early
- Reduces dependency on shared environments
- Enables parallel development
This approach significantly reduces reliance on brittle E2E tests and is now core to advanced qa testing services.
Service Virtualization and Test Isolation
By mocking dependent services:
- Teams test independently
- Failures are easier to diagnose
- Test environments become more stable
This isolation is a cornerstone of scalable quality engineering services for microservices.
AI-Driven Test Optimization
AI-driven testing platforms help enterprises:
- Identify redundant E2E tests
- Predict high-risk service interactions
- Prioritize test execution based on change impact
- Detect flaky tests automatically
As release velocity increases, AI becomes essential for maintaining quality without increasing cost.
Embedding End-to-End Testing into CI/CD Pipelines
Shift Left, But Also Shift Smart
Enterprises no longer run full E2E suites on every commit. Instead:
- Smoke E2E tests run early
- Critical flows run pre-release
- Full regression runs selectively
This approach ensures confidence without slowing pipelines—an outcome modern software testing services are designed to deliver.
Observability-Driven Validation
Testing and monitoring are converging. Enterprises validate:
- Logs, traces, and metrics during test execution
- Real system behavior instead of synthetic assertions
This improves defect detection while reducing false positives.
Security Considerations in End-to-End Microservices Testing
Why Security Cannot Be an Afterthought
Microservices expand the attack surface through:
- APIs
- Inter-service communication
- Shared infrastructure components
End-to-end testing must include security validation across service boundaries.
Role of a Penetration Testing Company
A specialized penetration testing company helps enterprises:
- Identify vulnerabilities across integrated services
- Test authentication, authorization, and data flow controls
- Simulate real-world attack scenarios in distributed systems
Leading enterprises align E2E functional testing with insights from a penetration testing company to ensure resilience and compliance.
read more : What is PET Injection Molding?
Data Signals Driving the Shift in Strategy
- Over 70% of enterprises report flaky E2E tests as a top QA challenge in microservices environments
- Organizations that reduce E2E test volume and increase contract testing report 40–50% faster release cycles
- Teams adopting AI-driven test optimization see up to 35% reduction in test maintenance effort
These trends reinforce why enterprises are modernizing software testing services for microservices at scale.
Governance, Compliance, and Audit Readiness
For regulated industries, end-to-end testing must demonstrate:
- Traceability across services
- Consistent enforcement of business rules
- Secure data handling across integrations
Well-structured quality engineering services generate audit-ready artifacts without slowing delivery.
Choosing the Right Enterprise Testing Partner
Enterprise leaders evaluate partners based on:
- Proven microservices testing expertise
- Strong API and contract testing capabilities
- AI-driven automation maturity
- Integration with DevSecOps
- Collaboration with a trusted penetration testing company
The right partner reduces complexity instead of adding process overhead.
Conclusion: Controlled End-to-End Testing Drives Enterprise Confidence
End-to-end testing remains essential in microservices—but only when applied strategically. Enterprises that limit E2E tests to critical business flows, strengthen service-level validation, and adopt modern software testing services avoid test chaos while accelerating delivery.
By combining advanced qa testing services, scalable quality engineering services, and security validation from a capable penetration testing company, organizations achieve faster releases, lower risk, and higher confidence in production.
FAQs: End-to-End Testing in Microservices
1. Is end-to-end testing still required in microservices architectures?
Yes, but it should focus on critical business journeys rather than exhaustive coverage.
2. How do qa testing services reduce flaky E2E tests?
Through contract testing, service virtualization, and smarter test selection.
3. What role do quality engineering services play in microservices testing?
They align automation, observability, and governance with business outcomes.
4. How does a penetration testing company support E2E testing?
By identifying security risks across integrated services and workflows.
5. How often should full E2E tests be executed?
Selectively—based on risk, release readiness, and business impact.